Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of illness and emergencies worldwide. With changing lifestyles, increasing stress levels, diabetes, high blood pressure, and smoking habits, coronary artery disease is being diagnosed at a younger age than ever before.
One of the most effective and life-saving treatments for blocked heart arteries is angioplasty. This minimally invasive procedure has transformed the way heart blockages are treated, allowing patients to recover faster and return to normal life sooner.
This detailed guide explains everything you need to know about angioplasty — including indications, procedure types, recovery, risks, costs, and frequently asked questions — under the care of Dr. Abhishek Kasha, Interventional Cardiologist.
What Is Angioplasty?
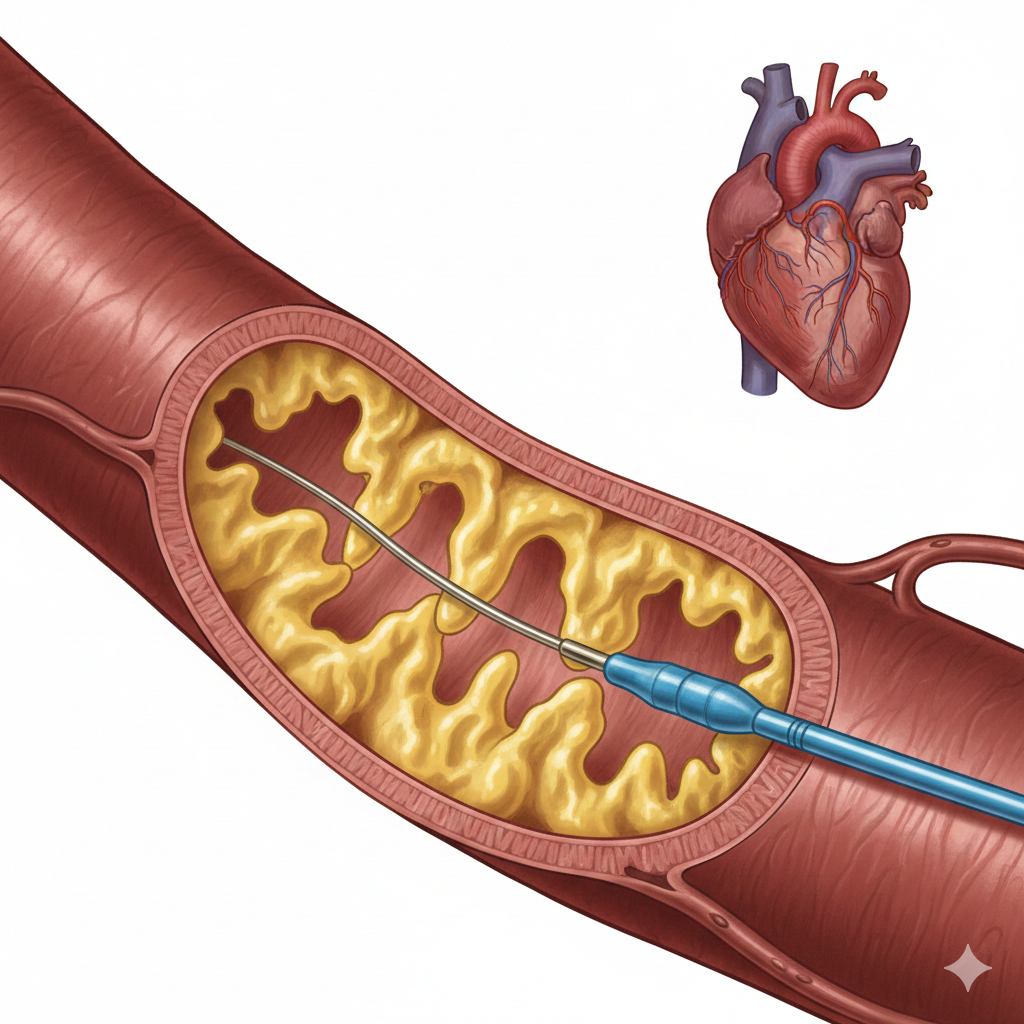
Angioplasty, medically known as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), is a procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
Over time, fatty deposits called plaque (cholesterol, calcium, and inflammatory cells) accumulate inside arteries. This restricts blood flow and can lead to:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Breathlessness
- Reduced exercise capacity
- Heart attack
Angioplasty restores blood flow without the need for open-heart surgery, often providing immediate relief from symptoms.
Why Do Heart Arteries Get Blocked?
Coronary artery disease develops gradually due to:
- High cholesterol levels
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Obesity and lack of physical activity
- Chronic stress
- Family history of heart disease
Early detection and timely intervention can prevent serious complications such as heart attacks.
Symptoms That May Indicate the Need for Angioplasty
A cardiology evaluation is recommended if you experience:
- Chest pain or tightness, especially during physical activity
- Pain radiating to the left arm, neck, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath on exertion
- Unusual fatigue
- Sudden chest discomfort with sweating or nausea
Prompt medical attention can be life-saving.
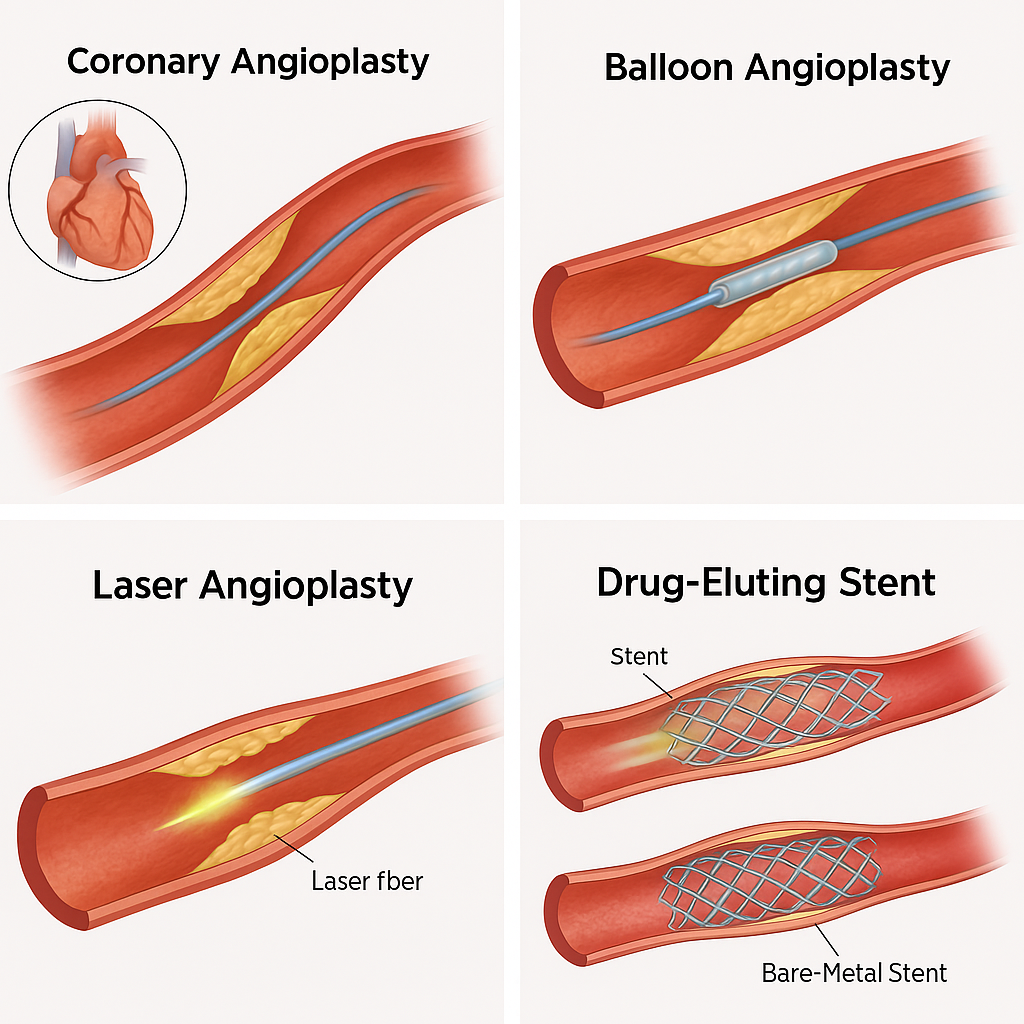
Types of Angioplasty Procedures
1. Coronary Angioplasty
This refers to angioplasty performed on the coronary arteries. A thin catheter is guided through an artery in the wrist or groin to reach the heart and treat the blockage.
Used in:
- Stable angina
- Unstable angina
- Acute heart attack
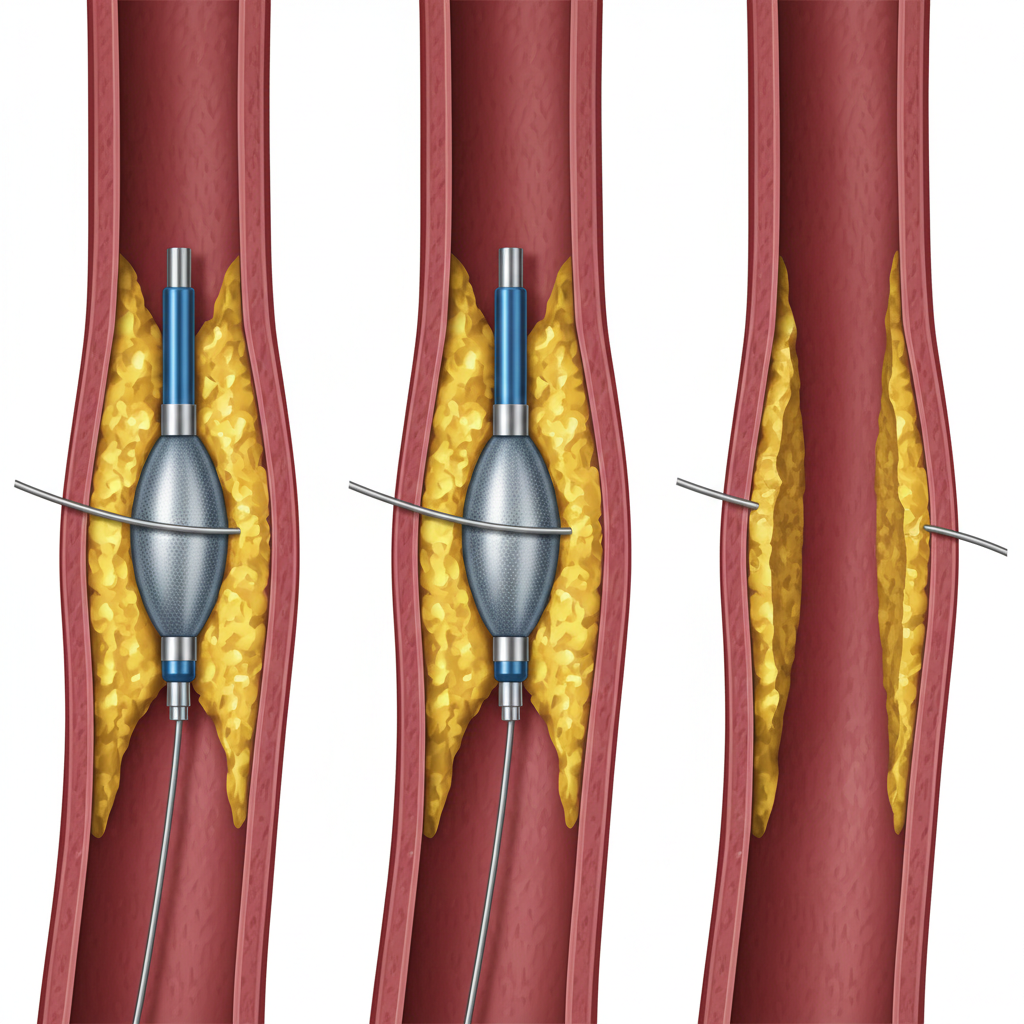
2. Balloon Angioplasty
A small balloon is inflated at the site of blockage to compress plaque against the artery walls and widen the blood vessel.
📌 In modern practice, balloon angioplasty is usually followed by stent placement.
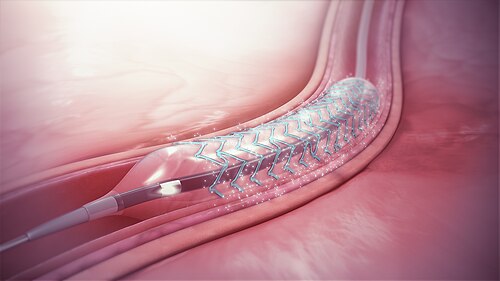
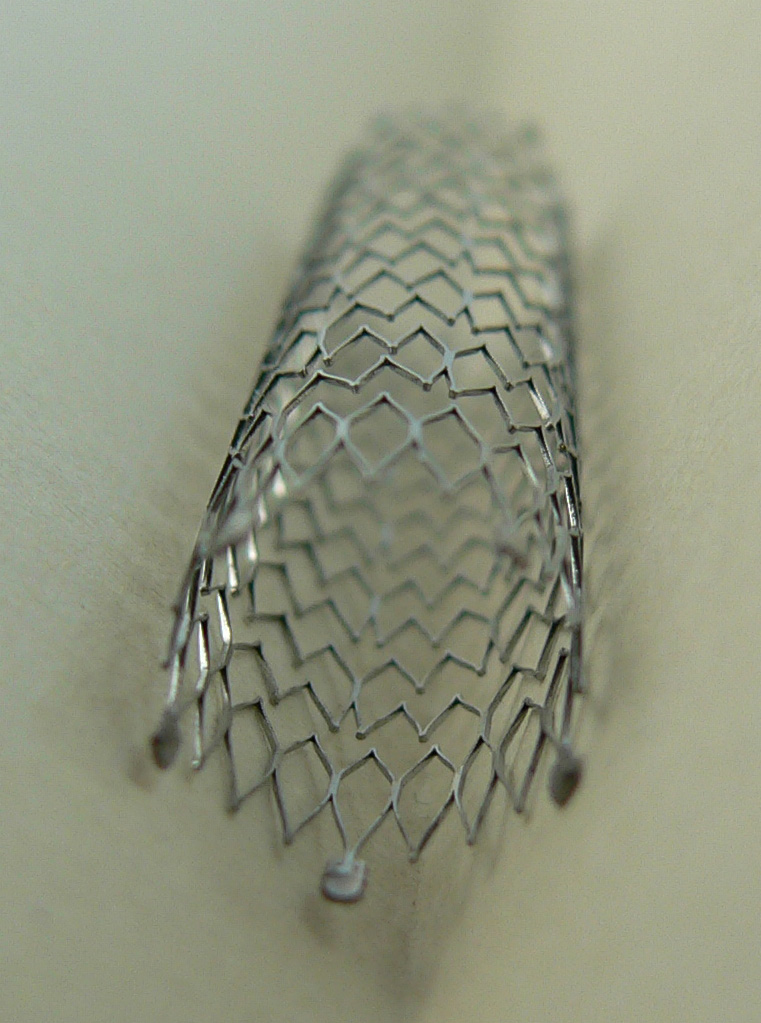
3. Drug-Eluting Stent (DES) Angioplasty
A drug-eluting stent is a metal mesh tube coated with medication that:
- Keeps the artery open
- Prevents excessive tissue growth
- Significantly reduces the risk of re-blockage
✅ Most commonly used stent today
✅ Excellent long-term results
4. Bare-Metal Stent (BMS)
An older type of stent without drug coating. It is now used only in specific clinical situations.
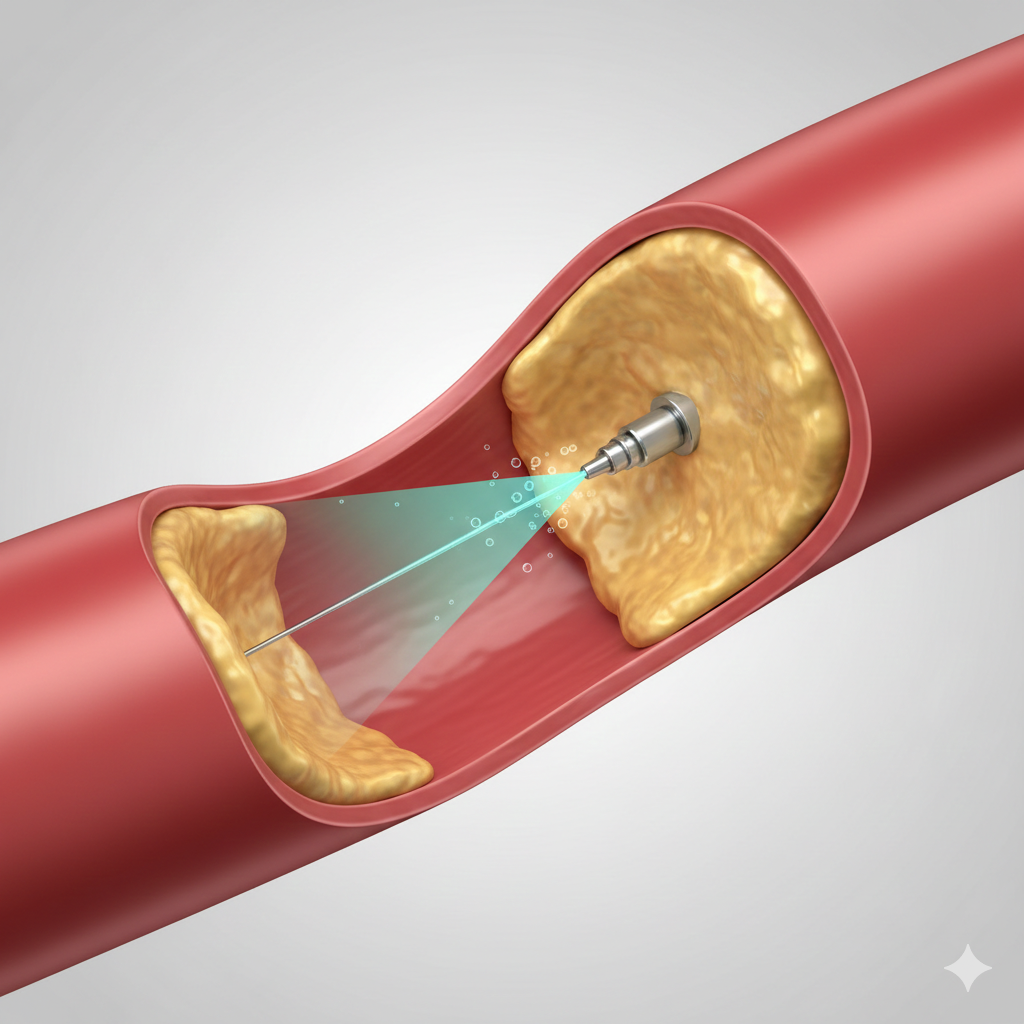
5. Laser Angioplasty
Laser angioplasty uses laser energy to break down hard or calcified plaque, especially when standard balloon techniques are insufficient.
Angioplasty Procedure: Step-by-Step
- Local anaesthesia is given (patient remains awake)
- Catheter inserted through wrist or groin artery
- Contrast dye injected to visualise blockages
- Balloon inflated at narrowed segment
- Stent placed to keep artery open
- Blood flow restored immediately
⏱️ Procedure duration: 30 minutes to 1.5 hours
Recovery After Angioplasty
- Hospital stay: 1–2 days
- Walking: Same day or next day
- Return to routine activities: 5–7 days
- Complete recovery: 2–3 weeks
Radial (wrist) access angioplasty allows faster mobilisation and fewer complications compared to traditional approaches.
Benefits of Angioplasty
✔ Rapid relief from chest pain
✔ Minimally invasive treatment
✔ No chest incision
✔ Short hospital stay
✔ Life-saving in heart attack
✔ Improved quality of life
Risks of Angioplasty
Although angioplasty is generally safe, possible risks include:
- Bleeding or bruising at catheter site
- Blood clot formation inside the stent
- Re-narrowing of the artery
- Reaction to contrast dye
These risks are significantly reduced when the procedure is performed by an experienced interventional cardiologist.
Life After Angioplasty
Angioplasty treats the blockage but does not cure heart disease. Long-term success depends on:
- Regular medications
- Control of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol
- Healthy diet
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management
- Avoiding smoking and tobacco
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is angioplasty a major surgery?
No. It is a minimally invasive procedure without opening the chest.
How long does a stent last?
Modern drug-eluting stents are designed to last a lifetime.
Is angioplasty painful?
Most patients experience minimal discomfort.
Can arteries block again after angioplasty?
Yes, if medications and lifestyle changes are not followed.
Is angioplasty safe for elderly patients?
Yes, with proper evaluation and expert care.
Can patients lead a normal life after angioplasty?
Yes, most patients return to an active, healthy lifestyle.
About the Doctor
Dr. Abhishek Kasha
Interventional Cardiologist
Specialist in Coronary Angiography & Angioplasty
Dr. Abhishek Kasha specialises in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease, including elective and emergency angioplasty procedures. His approach emphasises patient safety, precision, and long-term cardiovascular health.
Location: Tirupati
Consultation: By appointment